Pat Haran

Pat has been making flutes since 1990 on his website, he says:
My search for a flute led me to a Native American arts and crafts show at the Pueblo Grande Museum in Phoenix.
There I found Hopi artist and flute maker Ernie Northrup making river reed flutes in his booth. Ernie invited me to Tucson for a flute workshop he offered, and there I learned the basics of flute-making that Ernie's grandfather taught him growing up on the Hopi Mesas. Since then I have been making flutes

2018 Nr 037 bas F#
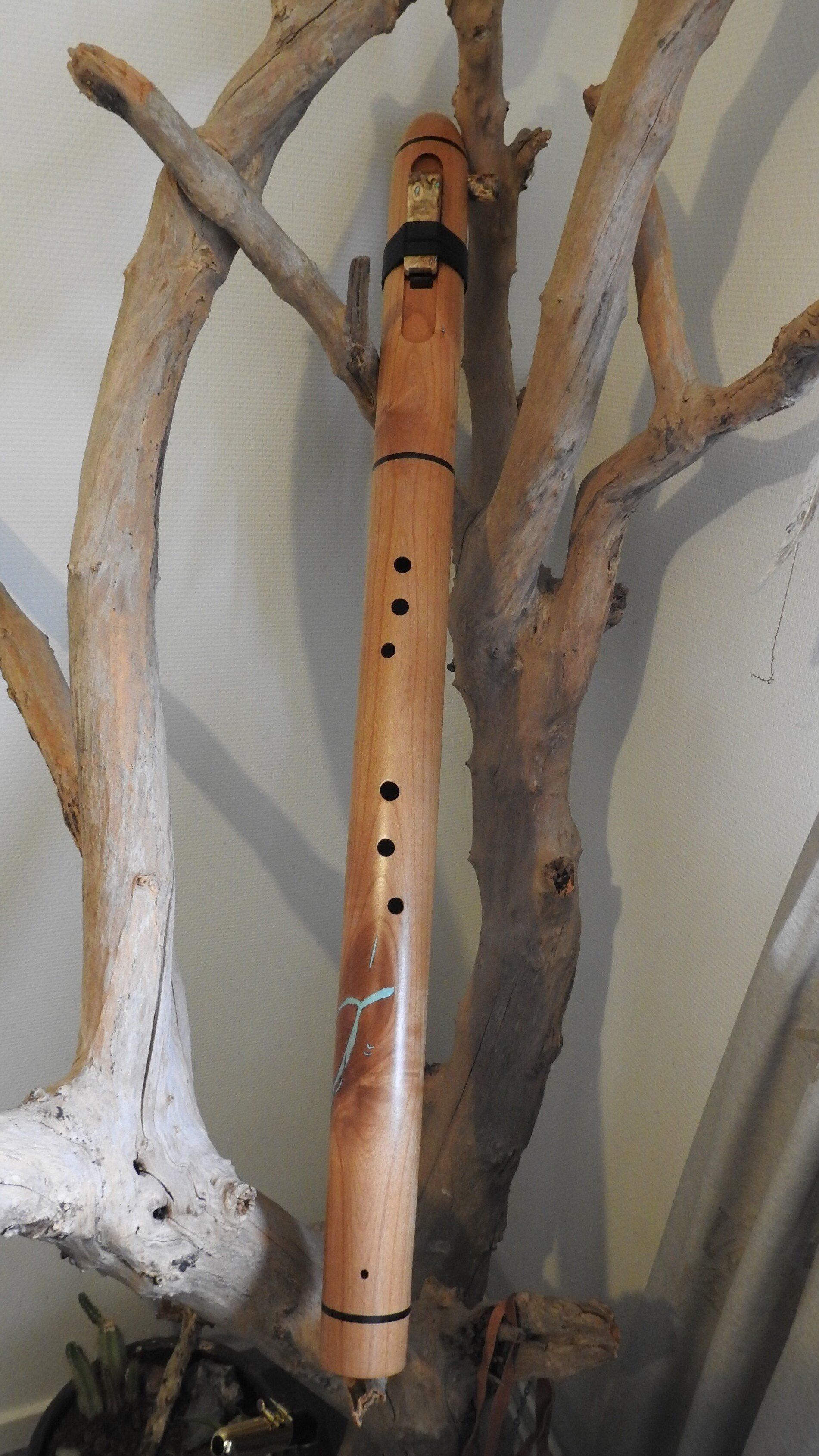

Use the flute often to give extra atmosphere to the deep sound
can you belong to the two songs number
Looking for a bass flute I came across a video on youtube where a flute player used a bass flute from Pat.
Soon I found his beautiful website the flute is made red Els and the mouthpiece and block of Burl wood

The flute has been modified because I play with my right hand above. Because I'm not big in stature and my neck easily hurts, playing the flute isn't easy. At an Aquarium store I bought this snake that bends in such a way that I can play more easily.
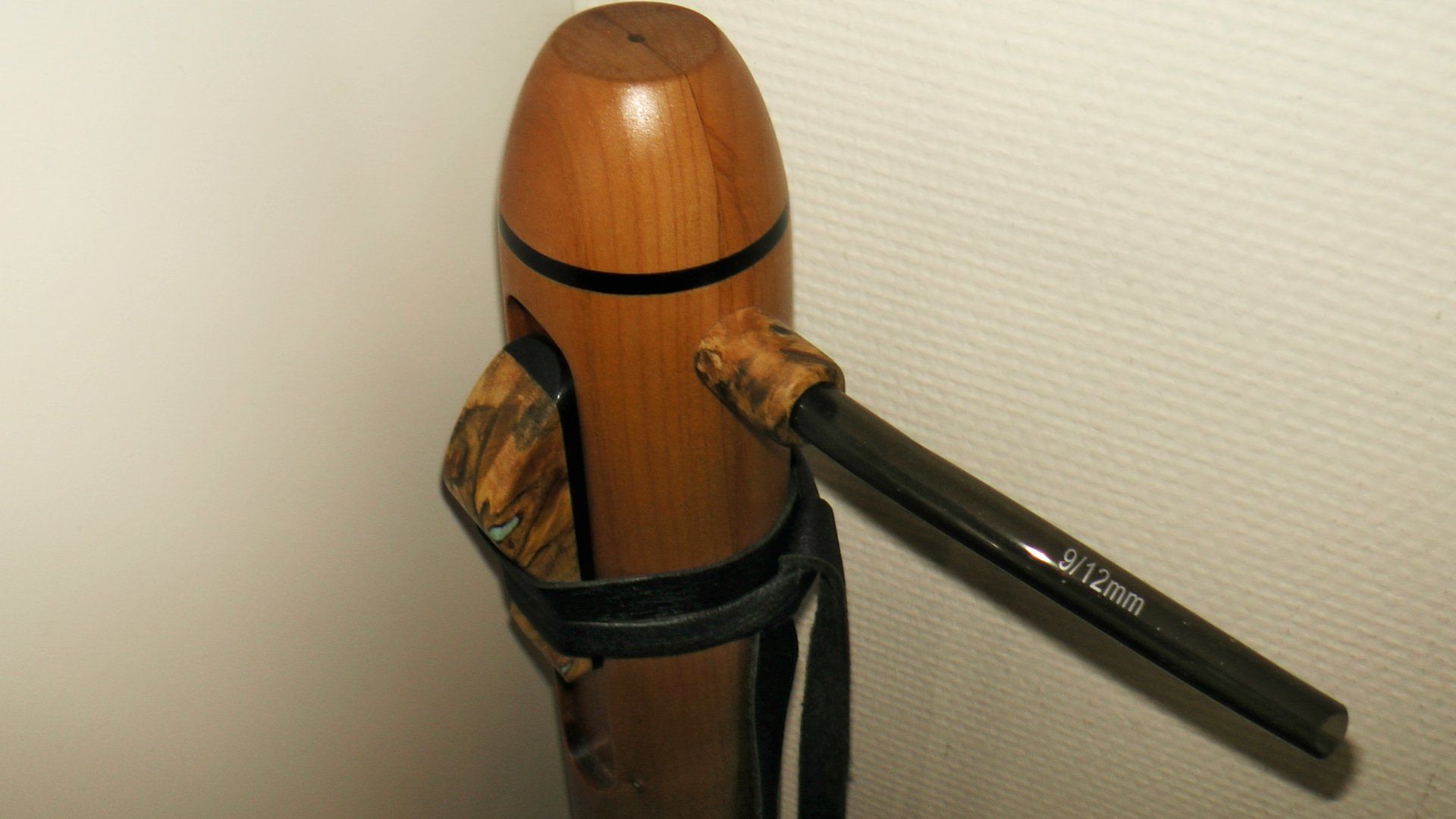

The material mouthpiece and block
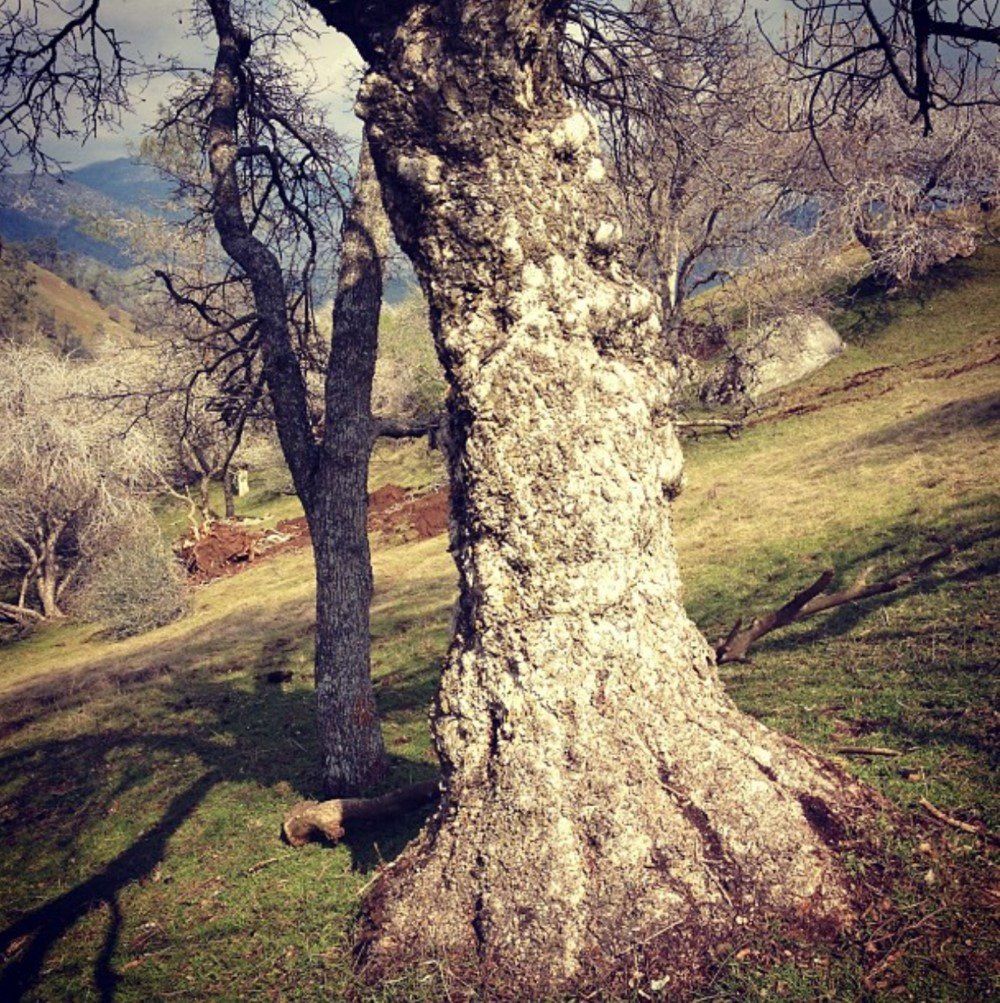
The block and mouthpiece These are made of Burlwood which comes from the California buckyeye.- Aesculus californica- California horse chestnut
Buckeyes spread quickly and yield a crop of nuts every year. Many believe that caring for the buckeyes is a responsibility passed on to us by the indigenous people who have used the buckeye tree for the past few thousand years.
However, this seed or nut contains a neurtoxin gylcoside aesculin, which is destructive to our red blood cells and may also be associated with rat poison. But all the leaves, shoots and flowers of the buckeye are poisonous, as is the fine sawdust.
Native Americans called the seed "hetuck," which translates to "buck eye" -- because the markings resemble a deer's eye. Many say that the Native Americans used the tree for medicinal purposes, such as snake bites, by cutting the bark from the base of the tree and making a poultice. They also crushed buckeye nuts and dumped the contents into rivers and streams to stun or kill fish. The smooth, straight, dense, yet flexible branches of the buckeye were also made for bows and firebows. 90 percent of the wood used from the tree comes from the root.
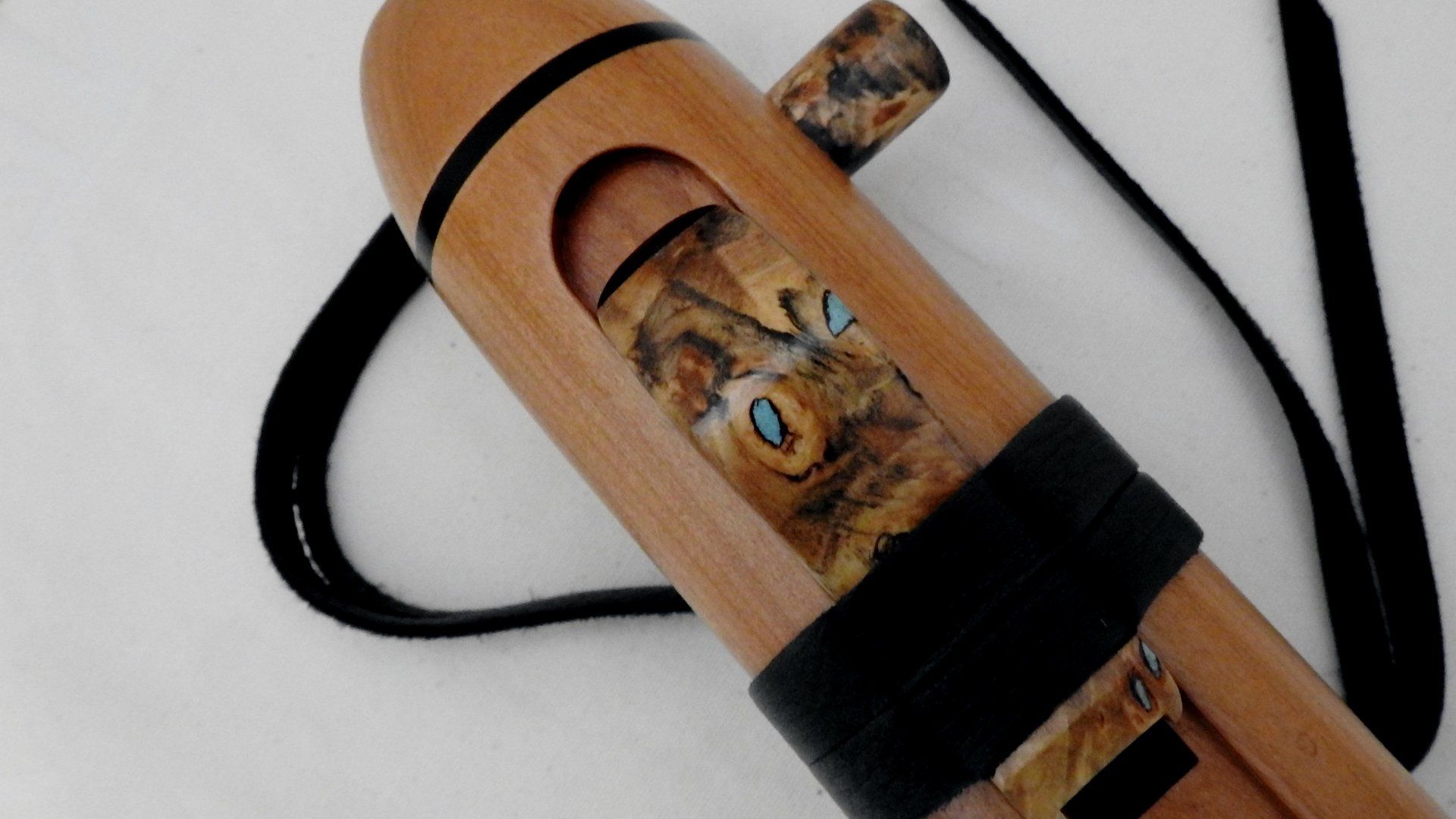



The material of the flute
Rode Els-Alnus rubra
Aboriginal people used the bark to dye basket material, wood, wool, feathers, human hair and skin. Depending on the technique used, the colors varied from black to brown to orange-red. Some coastal groups used the inner cambium layer of the tree as food. It is good wood for smoking meat. The wood was also used for carving objects such as bowls.